Basic Definition of Internet Governance
Internet Governance refers to the rules, policies, standards, and practices that coordinate and shape how the Internet is managed globally. It involves multiple stakeholders working together to ensure the Internet remains open, secure, and accessible for everyone.

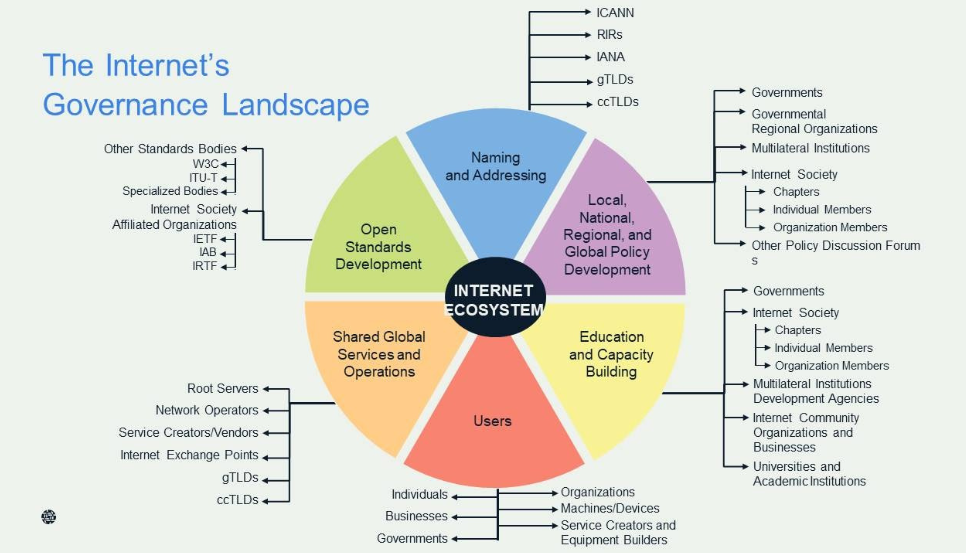
The Internet Governance Ecosystem
The Internet’s infrastructure is operated across borders and by a range of different stakeholders. It is a complex but robust ecosystem where each part of the Internet can rely on many other parts working together but often independently. (Internet Society, 2016)
Multistakeholder Model
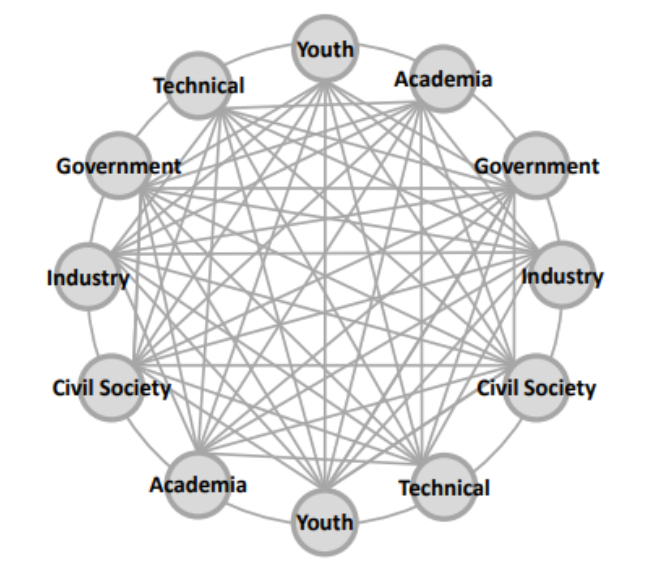
“A collaborative approach where different groups, including governments, private sector, civil society, academia, and technical community, work together to manage the Internet and address issues of interest.”
Key Stakeholders:
- Governments: Set policies and regulations.
- Private Sector: Develops technology and infrastructure.
- Civil Society: Advocates for users' rights and interests.
- Academia: Provides research and expertise.
- Technical Community: Ensures the technical operation and development of the Internet.
- Youth: Drive innovation and advocacy in Internet governance.
Internet Governance initiatives and organizations
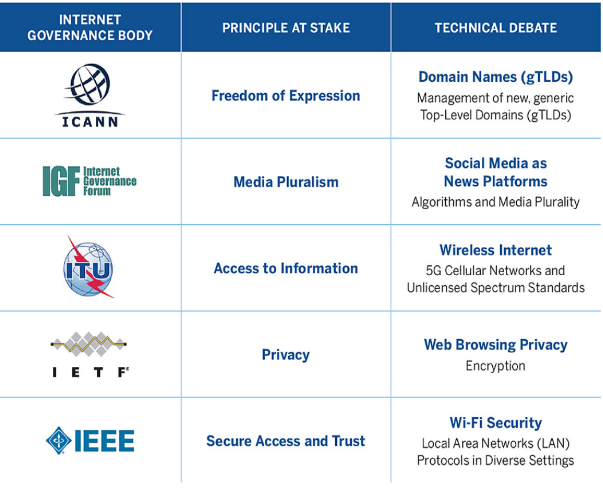
- Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN): A global organization responsible for coordinating the Internet's system of unique identifiers, such as domain names and IP addresses.
- Internet Society (ISOC): A nonprofit organization dedicated to promoting an open, globally connected, secure, and trustworthy Internet.
- United Nations International Telecommunication Union (ITU): A specialized UN agency responsible for issues related to information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Internet Governance Forum (IGF): A multistakeholder platform established by the United Nations to facilitate discussions on Internet governance.
- Internet Technical Advisory Committee (ITAC) to the OECD: A body that provides technical expertise and insights on Internet governance to the OECD.
- World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS): A UN-convened initiative aimed at promoting a global information society.
- World Conference on International Telecommunications (WCIT): A conference held under the ITU to review the International Telecommunication Regulations (ITRs).
- Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs): National and international agencies responsible for enforcing laws and regulations, including those related to cybercrime.
- National and Regional IGF Initiatives (NRIs): Local versions of the IGF, promoting discussions on Internet governance at national and regional levels.
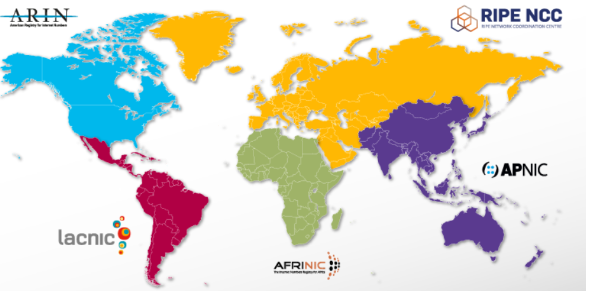
- RIRs: The five RIRs manage the allocation and registration of Internet number resources in different regions.
- Youth Initiatives: Programs aimed at involving young people in Internet governance discussions.
Global Bodies Governing Internet
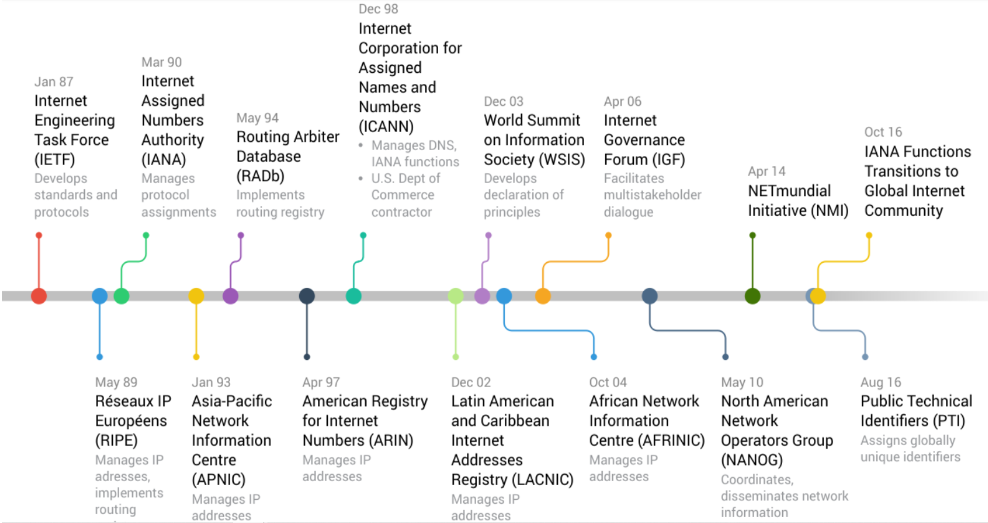
Internet Governance Timeline
Comparison of Different Types of Internet Governance Events
| Aspect | School of Internet Governance (SIG) | Internet Governance Academies | Internet Governance Forums (IGF) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Educate and build capacity on Internet governance topics | Provide specialized training and advanced understanding | Facilitate open dialogue on Internet governance |
| Participants | Students, young professionals, newcomers | Young leaders, policy makers, students | Governments, private sector, civil society, academia, technical community |
| Format | Intensive training sessions, workshops, lectures | Academic courses, seminars, practical exercises | Panel discussions, workshops, open forums, collaborative sessions |
| Focus | Foundational knowledge, skill development, hands-on learning | In-depth study, policy analysis, leadership skills | Policy dialogue, multi-stakeholder collaboration, global challenges |
| Example | Asia Pacific School of Internet Governance (APSIG), African School on Internet Governance (AfriSIG) | Asia-Pacific Internet Governance Academy (APIGA) | Global Internet Governance Forum (IGF), Asia Pacific Regional IGF (APrIGF) |